- a) What is the difference between Integer, Byte, and Real Number data types?
Integer: Integers are non-fractional, or whole numbers that can be positive, negative or zero. In Terrset, files having an integer data type can contain any whole numbers from -32768 to +32767.
Byte: A Byte is a sub-type of integer that can only have positive values from 0-255.
Real Number: Real numbers are values of a continuous quantity. Real numbers can be thought of as points along an infinitely long line called a ‘Number Line’. Real numbers include all the rational numbers, the irrational numbers, as well as the transcendental numbers such as pi or e. In simple terms, real numbers are numbers that may contain fractional parts.
b) What is the difference between ASCII and UNICODE, and why is ASCII a more common GIS data type?
ASCII is an acronym that stands for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange. ASCII allows digital representation of alphabetic characters, numbers and symbols. An ASCII character uses 1 byte (8 bits) of memory.
UNICODE requires 2 bytes (16 bits) per character and was designed to handle non-US alphabet systems such as Chinese and Greek.
ASCII is a subset of UNICODE, but it is more commonly used in GIS because each ASCII character requires only half as much memory as a UNICODE character. However, in TerrSet, UNICODE is accepted for text layers because the software is used worldwide.
c) Give an example of when a quantitative bipolar palette is appropriate. Give an example of when a quantitative ramp palette is appropriate. Give an example of when a qualitative palette is appropriate.
Quantitative Bipolar Palette: Used to represent two distinct values represented by two color groups. A quantitative bipolar palette could be applied to a map depicting areas where the public can access clean water and areas clean water is unavailable.
Quantitative Ramp Palette: Representing an increase in value of some variable. A quantitative ramp palette could be applied to pixels representing elevation values in a digital elevation model (DEM)
so that variations in elevation over large areas are more perceptible to the map user.
Qualitative Palette: Represents various values that each have distinct attributes. A qualitative palette could be applied a map detailing the various geologic materials found within a region.
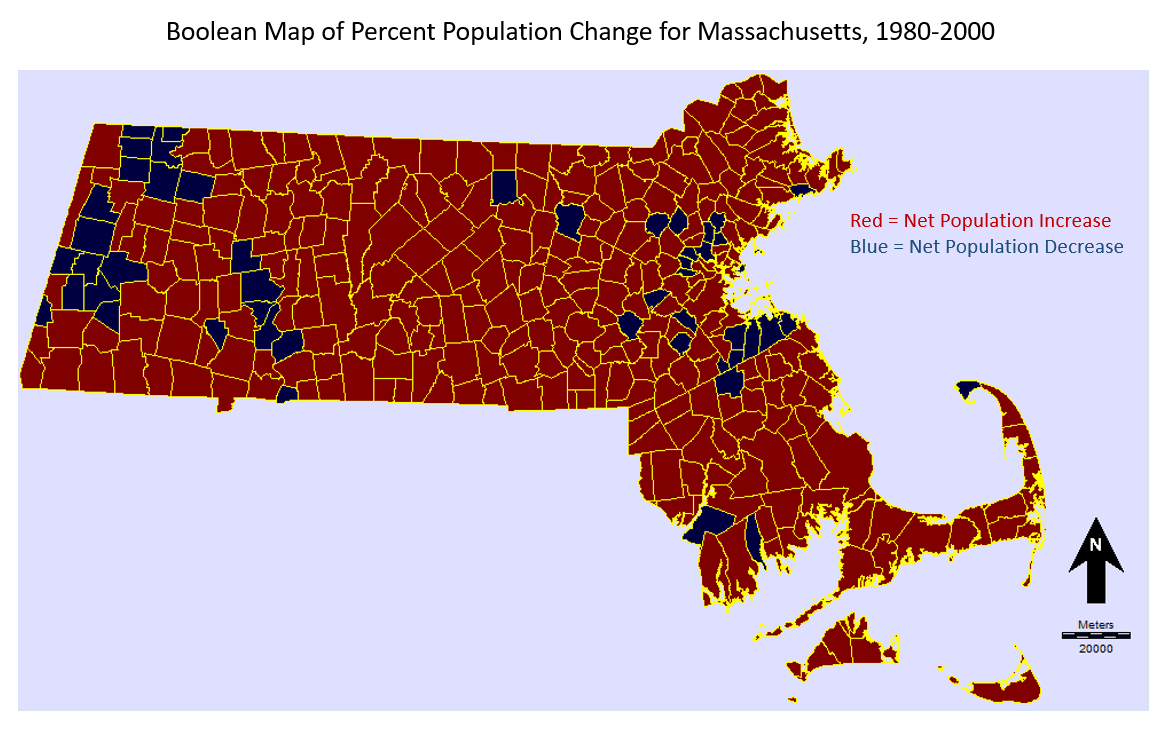
2. a) In this exercise, you classified Massachusetts census areas into quantiles. What is a quantile and why is it sometimes advantageous to use them?
Quantiles are intervals, or ‘cut points’ which are distributed over a range of values, such as a population distribution across geographic space. Quantiles are advantageous for organizing and displaying a dataset by ranking values categorically.
Give another example of when quantiles would be a better classification method than a linear color ramp.
One application would be for classifying the average household income in a city or county. For example, one colour could represent an average income of less than $12,000 annually, followed by another color representing an average income of anywhere between $12,000-24,000, and so on.
b) What is the name of the town in the database table with the greatest population in the year 2000? (Select the field, then click Query > sort Descending).
The town with the greatest population in 2000 is Boston, Massachusetts, which had a population of 588,957.
c. What is the 1980 population of the town with the greatest area?
The town with the greatest area in 1980 is Plymouth, Massachusetts, which had a population of 38,384.
3. a) How many towns are there in total? (Look at ‘Records’ in the bottom panel of the Database Workshop window).
There are 351 towns according to the records panel.
How many towns have a population change greater than zero between both 1980-1990 and 1990-2000?
There are 249 towns that experienced a population change of greater than zero between both 1980-1990 and 1990-2000.
b) You calculated a new field [PopCh80_00] in the ‘Calculate’ section of the exercise. What is this and what are the units of measurement?
This represents the difference in population from 1980 to 2000 represented as a ratio to the population in the year 2000, expressed as a percent. In other words, the calculation gives the percent increase or decrease of the population in each town over the 20 year period between 1980 to 2000.
c) In section ‘h’ of the exercise, you create a choropleth (quantitative classified colored polygons) map. Reclassify this into 16 Standard Scores (standard deviations). Use the cursor inquiry tool to find the name of the town with the greatest population decline. What is the name of this town?
Harvard.
Why do you think it has experienced such a drastic population decline between years 1980 and 2000?
The drastic population decline can likely be attributed to the closure of a large military installation in Fort Devens in 1996. This resulted in the departure of military personnel and their families. A large part of the military installation was located in the town of Harvard. (Wikipedia)
d) Create a map composition of the map you created in 3c, using MS PowerPoint. Submit this as a separate page, including all necessary map elements.

e) In section ‘i’, look through the different tabs in the Massachusetts database file. How many hospitals and schools are in Massachusetts, according to the database file?
According to the database file, there are 145 Hospitals and 2521 Schools in Massachusetts.
f) Which town experienced the greatest growth between years 1990 and 2000? Why do you think this is?
Boston experienced the greatest growth between 1990 and 2000. The population increase during these years could be related to international immigration. Another possibility is that people are attracted to Boston for entrepreneurial reasons- the city has one of the largest economies in the United States.
g) Complete the ‘challenge’ section on page 55 of the tutorial.